The W and Z chromosome studies of the silkworm, Bombyx mori

Research members: Hiroaki Abe PhD.
Research fields: Animal life science, Biological Science, Genome science
Departments: Institute of Agriculture
Keywords: silkworm, Bombyx mori, W chromosome, sex chromosome, transposable element, retrotransposon
Summary
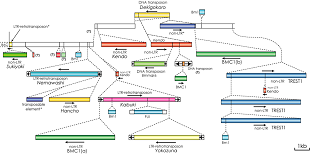
Sex chromoosmes of the silkworm, Bombyx mori, are designated as ZW (XY) for females and ZZ (XX) for males. The female mode of development is determined by the presence of a single W chromosome. Therefore, it is presumed that the female-determining gene (Fem) is present on the W chromosome. Until date, 12 W-specific random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers have been identified on the normal W chromosome. We have compared the W-translocation chromosomes with normal W chromosome. The T(W;3)Ze (the sex-limited Zebra strain) chromosome lacked 2 W-specific RAPD markers, indicating that the region containing these two W-specific RAPD markers has been deleted. Additionally, we have investigated T(W;2)Y (the sex-limited Yellow-cocoon strain). The T(W;2)Y chromosome lacked 11 such markers. These results indicate that the W chromosomes of the sex-limited strains are products of reciprocal translocation accompanied by deletio, and an extremely limited region is required to determine femaleness. No genes for morphological traits have been mapped to the W chromosome. Contrary, Z chromosome is rich in genes. Many long terminal repeat (LTR) and non-LTR retrotransposons, retroposons, DNA transposons, and their derivatives, had accumulated as strata on the W chromosome. It is notable that some of these transposable elements contained the Bombyx short interspersed element (Bm1) sequences in the elements. On the other hand, the transposable elements on the Z chromosome were excluded by unequal crossing over or intra-element homologous recombination between LTRs.
Reference articles and patents
Abe, H., Y. Sugasaki, T. Terada, M. Kanehara, F. Ohbayashi, T. Shimada, S. Kawai, K. Mita and T. Oshiki (2002): Nested retrotransposons on the W chromosome of the wild silkworm Bombyx mandarina. Insect Molecular Biology, Vol. 11, 307-314.
Abe, H., M. Seki, F. Ohbayashi, N. Tanaka, J. Yamashita, T. Fujii, T. Yokoyama, M. Takahashi, Y. Banno, K. Sahara, A. Yoshido, J. Ihara, Y. Yasukochi, K. Mita, M. Ajimura, M. G. Suzuki, T. Oshiki and T. Shimada (2005): Partial deletions of the W chromosome due to reciprocal translocation in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Molecular Biology Vol. 14, 339-352.
Abe, H., T. Fujii, T. Yokoyama, M. Seki, M. Ajimura, K. Mita, N. Tanaka, M. Takahashi, Y. Banno, Y. Yasukochi, T. Oshiki, M. Nenoi, T. Ishikawa and T. Shimada (2008): Identification of female-determining region of the W chromosome in Bombyx mori. Genetica Vol. 133, 269-282.
The International Silkworm Genome Consortium (2008): The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Vol. 38, 1036-1045.
Abe, H., T. Fujii, T. Shimada and K. Mita (2010): Novel non-autonomous transposable elements on the W chromosome of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Journal of Genetics 89, 375-387.
Fujii, T., T. Fujii, S. Namiki, H. Abe, T. Sakurai, A. Ohnuma, R. Kanzaki, S. Katsuma, Y. Ishikawa and T. Shimada (2011): Sex-linked transcription factor involved in a shift of sex-pheromone preference in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) 108 (44), 18038-18043.
Fujii, T., H. Abe, M. Kawamoto, Y. Banno and T. Shimada (2015): Positional cloning of the sex-linked giant egg (Ge) locus in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Molecular Biology Vol 24, 213-221.
(総説)
Goldsmith, M. R., Shimada, T. Abe, H. (2005): Genetics and Genomics of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Annual Review of Entomology Vol. 50, 71-100.
阿部広明・藤井 告・三田和英・嶋田 透(2012):カイコW染色体研究の歴史と最近の分子生物学的研究. 蚕糸・昆虫バイオテック 81, 187-199.
(単行本)
Abe, H., Fujii, T. and Shimada , T. (2010): Sex Chromosomes and Sex determination in Bombyx mori. In “Molecular Biology and Genetics of the Lepidoptera (Contemporary Topics in Entomology)” Crc Pr I Lic pp. 65-87.(ISBN: 978-1420060147).
Abe, H., Fujii, T. and Chandrasekar R. (2014): The recent progress of the W and Z chromosome studies of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. In “Short Views on Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Vol (1) ” Published by International Book Mission, Academic Publisher, South India. pp. 291-316. (ISBN: 978-1-63315-205-2 (USA)).
Contact
University Research Administration Center(URAC),
Tokyo University of Agriculture andTechnology
urac[at]ml.tuat.ac.jp
(Please replace [at] with @.)
